简单介绍如何使用Python的Flask框架来创建一个RESTful的API接口
RESTful RESTful是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,提供了一组设计原则和约束条件。
它的特点有:
每一个URI代表一种资源 客户端使用GET、POST、PUT、DELETE这4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作:GET用来获取资源,POST用来新建资源(也可以用于更新资源),PUT用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源 通过操作资源的表现形式来操作资源 资源的表现形式是XML或者HTML,或者JSON 客户端与服务端之间的交互在请求之间是无状态的,从客户端到服务端的每个请求都必须包含理解请求所必需的信息 模块 flask :Python的微框架
Flask-Migrate :使用Alembic的Flask应用进行SQLAlchemy数据库迁移
Flask-RESTful :Flask的扩展,可快速构建REST API
Flask-SQLAlchemy :Flask扩展,增加了对SQLAlchemy的支持
Flask-Script :提供了在Flask中编写外部脚本的支持
psycopg2 :Python的PostgreSQL API
marshmallow :ORM/ODM/框架无关的库,用于复杂数据类型(如对象)和Python数据类型转换
flask-marshmallow :Flask和marshmallow的中间层
代码 config.py:全局配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import osbasedir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) SQLALCHEMY_ECHO = False SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS = True SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = "postgresql://postgres:password@localhost/api_test"
app.py:配置flask、添加路由
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from flask import Blueprintfrom flask_restful import Apifrom resource.Hello import HelloResourcefrom resource.Category import CategoryResourceapi_bp = Blueprint('api' , __name__) api = Api(api_bp) api.add_resource(HelloResource, '/hello' , endpoint='hello' ) api.add_resource(CategoryResource, '/category' , '/categories' , endpoint='category' )
run.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 from flask import Flaskfrom flask_migrate import Migrate, MigrateCommandfrom flask_script import Managerfrom model import dbfrom app import api_bpdef create_app (config_filename) : app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config_filename) app.register_blueprint(api_bp, url_prefix='/v1' ) db.init_app(app) return app app = create_app('config' ) migrate = Migrate(app, db) manager = Manager(app) manager.add_command('db' , MigrateCommand) if __name__ == '__main__' : manager.run()
model.py :模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 from flask_marshmallow import Marshmallowfrom flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemyfrom marshmallow import fields, post_loaddb = SQLAlchemy() ma = Marshmallow() fields.Field.default_error_messages = { 'required' : '缺少必要数据' , 'null' : '数据不能为空' , 'validator_failed' : '非法数据' } fields.Integer.default_error_messages = { 'invalid' : '不是合法整数' } class Category (db.Model) : __tablename__ = 'category' id = db.Column(db.Integer, autoincrement=True , primary_key=True ) name = db.Column(db.String(32 )) def __init__ (self, name) : self.name = name class CategorySchema (ma.Schema) : id = fields.Integer() name = fields.String(required=True ) @post_load def make_category (self, data, **kwargs) : """反序列化的时候直接返回对象而不是字典""" return Category(**data) class Meta : ordered = True
resource/Hello.py
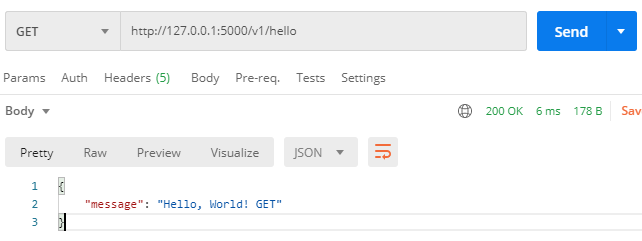
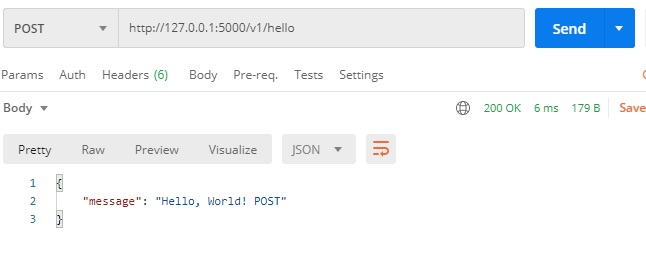
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from flask_restful import Resourceclass HelloResource (Resource) : def get (self) : return {"message" : "Hello, World! GET" } def post (self) : return {"message" : "Hello, World! POST" }
resource/Category.py
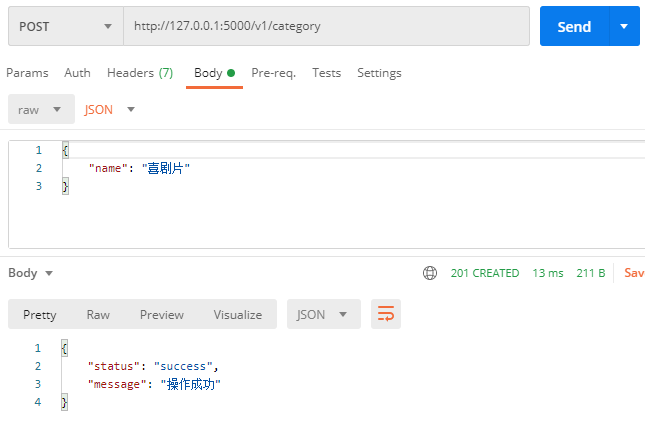
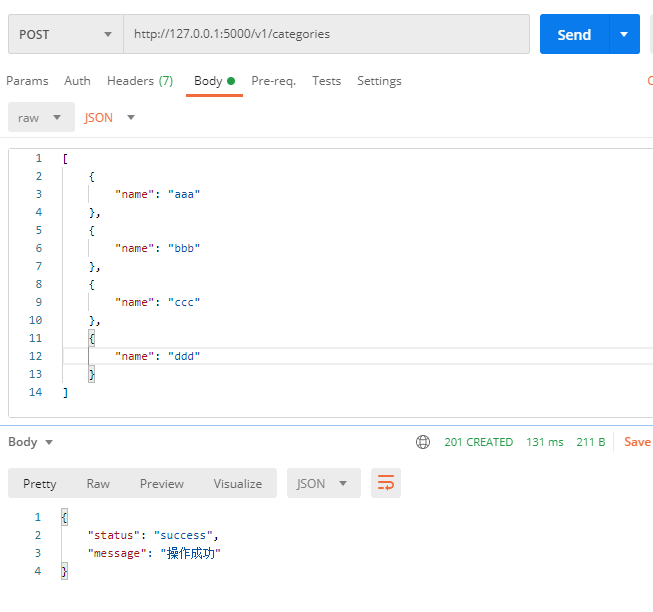
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 from flask import requestfrom flask_restful import Resource, abortfrom marshmallow import ValidationErrorfrom model import Category, CategorySchema, dbcategory_schema = CategorySchema() categories_schema = CategorySchema(many=True ) class CategoryResource (Resource) : def get (self, cid=None) : if 'category' in request.path: if not cid: return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : '参数错误' }, 400 else : category = Category.query.filter_by(id=cid).first() result = category_schema.dump(category) return {'status' : 'success' , 'data' : result}, 200 elif 'categories' in request.path: categories = Category.query.all() result = categories_schema.dump(categories) return {'status' : 'success' , 'data' : result}, 200 else : abort(404 ) def post (self) : json_data = request.get_json() if not json_data: return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : '参数错误' }, 400 try : if 'category' in request.path: category = category_schema.load(json_data) old_category = Category.query.filter_by(name=category.name).first() if old_category: return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : '数据已存在' }, 400 db.session.add(category) db.session.commit() return {'status' : 'success' , 'message' : '操作成功' }, 201 elif 'categories' in request.path: categories = categories_schema.load(json_data) for category in categories: old_category = Category.query.filter_by(name=category.name).first() if old_category: return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : '%s:数据已存在' % old_category.name}, 400 db.session.add_all(categories) db.session.commit() return {'status' : 'success' , 'message' : '操作成功' }, 201 else : abort(404 ) except ValidationError as e: return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : e.messages}, 400 def delete (self, cid=None) : if 'category' in request.path and cid: category = Category.query.filter_by(id=cid).first() db.session.delete(category) db.session.commit() return 204 else : return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : '参数错误' }, 400 def put (self, cid=None) : if 'category' in request.path and cid: json_data = request.get_json() if not json_data: return {'status' : 'failed' , 'message' : '参数错误' }, 400 old_category = Category.query.filter_by(id=cid).first() if old_category: category = category_schema.load(json_data) old_category.name = category.name db.session.commit() return {'status' : 'success' , 'message' : '操作成功' }, 201 abort(404 ) else : return '' , 204
数据迁移
1 2 3 $ python3 run.py db init $ python3 run.py db migrate $ python run.py db upgrade
启动服务
测试接口 GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/hello
POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/hello
POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/category
POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/categories
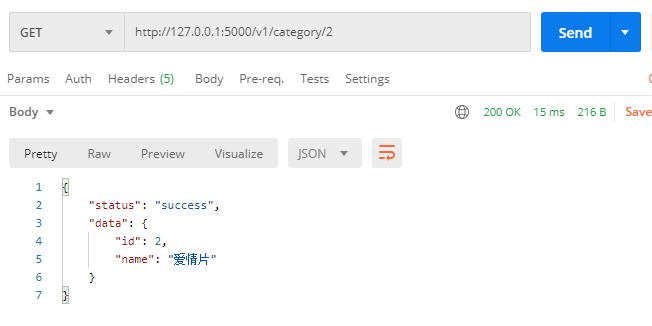
GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/category/<id>
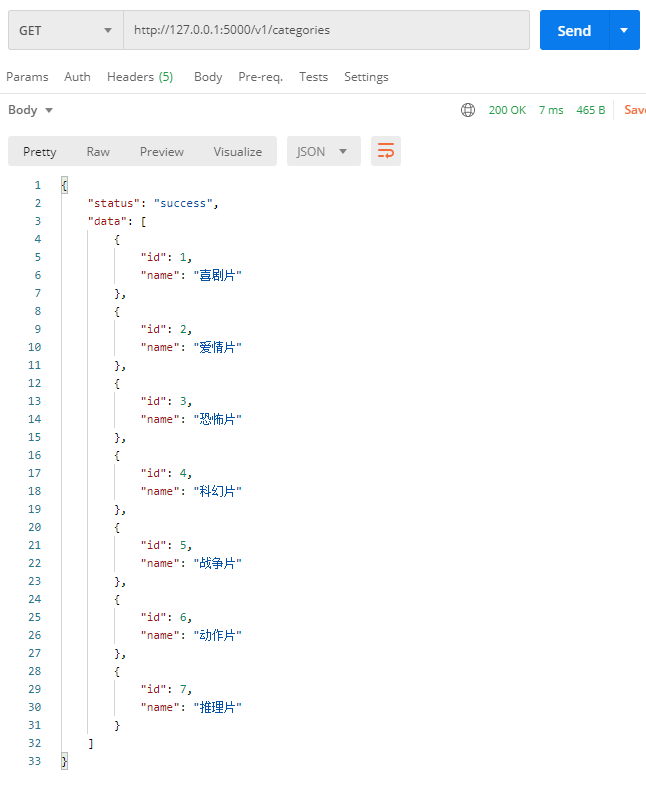
GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/categories
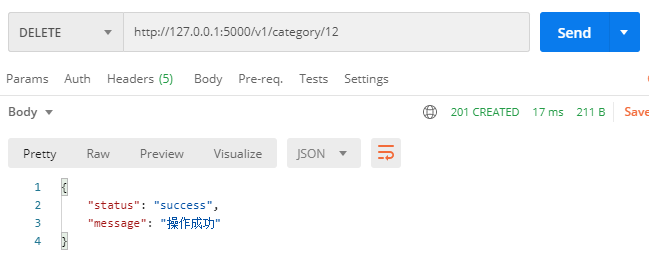
DELETE http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/category/<id>
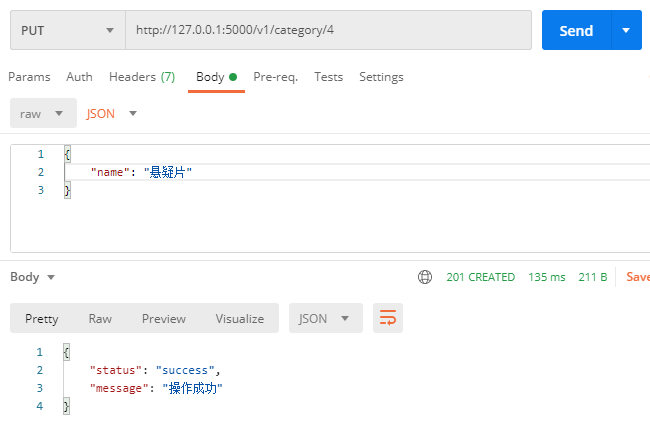
PUT http://127.0.0.1:5000/v1/category/<id>
总结 RESTful API的开发和使用,无非是客户端向服务器发请求(request),以及服务器对客户端请求的响应(response)
响应这些request时,常用的Response要包含的数据和状态码(status code)
当GET和PUT请求成功时,要返回对应的数据,及状态码200,即SUCCESS 当POST创建数据成功时,要返回创建的数据,及状态码201,即CREATED 当DELETE删除数据成功时,不返回数据,状态码要返回204,即NO CONTENT 当GET 不到数据时,状态码要返回404,即NOT FOUND 任何时候,如果请求有问题,如校验请求数据时发现错误,要返回状态码 400,即BAD REQUEST 当API 请求需要用户认证时,如果request中的认证信息不正确,要返回状态码 401,即NOT AUTHORIZED 当API 请求需要验证用户权限时,如果当前用户无相应权限,要返回状态码 403,即FORBIDDEN 最后,关于Request 和 Response,不要忽略了http header中的Content-Type。以json为例,如果API要求客户端发送request时要传入json数据,则服务器端仅做好json数据的获取和解析即可,但如果服务端支持多种类型数据的传入,如同时支持json和form-data,则要根据客户端发送请求时header中的Content-Type,对不同类型是数据分别实现获取和解析;如果API响应客户端请求后,需要返回json数据,需要在header中添加Content-Type=application/json
本文只是介绍怎样简单开发一个能用的api服务,如果要开发一个好用、美观的RESTful API服务,还需要更多的知识,更多相关知识可以看看这篇文章:应用Flask框架设计RESTFUL API接口